Accounting School blog established with an aim to provide provide free accounting, finance, management, tax and audit study material for accounts professionals as well as to students.
Wednesday, February 5, 2020
Accounting Basis and Policies
Accounting policies are the specific accounting bases judge by business enterprises to be most appropriate to their circumstances and adopted by them for the purpose of preparing their financial accounts.
Accounting basis are the various methods which have been developed for applying fundamental accounting concepts to financial transactions and to items in financial statements. Accounting bases are used for constructing accounting figures which are variable. These are methods developed for determining the;
Accounting periods in which revenues and costs should be recognised in the profit and loss account.
Amount at which material items should be stated in the balance sheet.
Example of Accounting Basis
Let’s suppose that a business unit is required to provide for depreciation of its fixed asset and stock valuation at the end of the each accounting period.
So, that, the following the accrual or matching concept;
Stock items can be set out against the sales proceeds of those items in future accounting period.
Example
Stock on actual value $15,000 Revalue at $ 17,780 on sales price
Assets can be shown at their carrying values in the Balance Sheet.
Example
Asset on cost value $80,000 on Carrying value after Depreciation of 10%
$80,000X10/100=$8,000 $72,000
Tuesday, February 4, 2020
Accounting Equation Examples
Example No.1
Let’s assume that ABC introduces / invest money in business i.e (Capital/Owner Equity) for $ 100 on December 31, 2019, ABC’s accounting equation is;
Example No.2
Purchased plant on credit for $500.
Example No.3
Purchased machine on credit $2,500.
Example No.4
Creditor paid off by cheque for $4,000.
Example No.5
Drawings by arranging bank overdraft for
$4,700.
Example No.6
Drawings of cash $ 15,000.
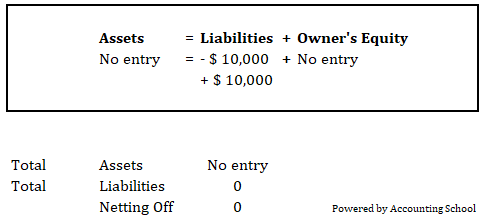
Example No.7
Creditors paid-off by arranging loan $
10,000.
Example No.8
Further capital introduced to pay-off
creditors $7,500.
Monday, February 3, 2020
What is Accounting Equation?
1- It is the basis of double entry
system of accounting.
2- It says that every transaction have two side effects.
3- Recording of two aspects of each transaction.
4- Assets and liabilities are two independent variables.
5- Capital is the dependent variable.
2- It says that every transaction have two side effects.
3- Recording of two aspects of each transaction.
4- Assets and liabilities are two independent variables.
5- Capital is the dependent variable.
Accounting transaction may affect both sides
of the equation by the same amount or on one side of the equation only, by both
increasing and decreasing it by equal amount and thus netting to ZERO.
Let’s assume that ABC introduces / invest
money in business i.e (Capital/Owner Equity) for $ 100 on December 31, 2019, ABC’s
accounting equation is;
Basic Accounting Principles
Basic accounting principles are accounting
standards that have been generally accepted and have pervasive impact on the
form and content of financial statements.
Duality
Duality is the basic characteristics of
accounting transaction which is embodied in double entry system. The claims against
assets of a business are by the creditors and the owners. Therefore, at any point of time,
the total assets of a business are equal to its total liabilities. Liabilities to outsiders are known as
liabilities, but liability to the owners in accounting is referred as capital.
This concept expresses the relationship that
exists among assets, liabilities and the capital, in the form of an accounting
equation which is expressed in the following simplest form as
ASSETS – LIABILITES = CAPITAL
OR
ASSETS = LIABILITES + CAPITAL
Sunday, February 2, 2020
Going Concern
It is not possible to determine in
advance the life-span of business unit. Accounting is based on the assumption that
the business unit will be operating for long. When business is started, it is
assumed that business will not be dissolved in the near future.
Profit & loss, balance sheet is
drawn up on the assumption that the business will continue functioning in the foreseeable
future.
Accounting system provides the continuous
record of business unit.
Business unit will continue its
operations under same economic conditions.
It is not assumed that business unit
will be profitable as long as it exists.
FACTOR TO
DETERMINE BUSINESS UNIT AS GOING CONCERN
a. Business must have sufficient liquid
assets i.e (cash, stock, bonds etc)
b. Shortage of liquid assets may lead to
the risk of insolvency.
Capital Structure
a. Business must have sound capital
structure.
b. Long term funds and short term
financing to overcome difficulties.
Market
a. Business unit must have strong market demand
product.
b. Goods, services or trading products
should have market demand.
Management Ability
a. Business unit should be managed
efficiently, effectively.
b. Must have clear objective to increase
the wealth of owners.
c. Plan, procedure, policies and practices
should be used.
Basic Accounting Assumptions
Ø Accounting Entity
1. Sole
proprietor
4. Non-profit making organization
 We
must for the book-keeping, keep the owner and his business quite separate. Only
those economic affect the business unit are recorded. Assuming that business
unit is a separate entity, accounting records are kept only from the point of
view of the business unit and not the owners.
We
must for the book-keeping, keep the owner and his business quite separate. Only
those economic affect the business unit are recorded. Assuming that business
unit is a separate entity, accounting records are kept only from the point of
view of the business unit and not the owners.
To ascertain the return on capital employed.
To ensure proper use of funds.
To hold title to property in the name of the firm.
To enter into business with outsiders.
Stability in the value of money
Ø Money Measurement
Ø Going Concern
Ø Accounting Period
Accounting
Entity
A
business entity is an organization of persons to accomplish an economic goal. An
entity is defined as those undertakings under the control of a single
management as;
2. Partnership
firm
3. A
company4. Non-profit making organization
 We
must for the book-keeping, keep the owner and his business quite separate. Only
those economic affect the business unit are recorded. Assuming that business
unit is a separate entity, accounting records are kept only from the point of
view of the business unit and not the owners.
We
must for the book-keeping, keep the owner and his business quite separate. Only
those economic affect the business unit are recorded. Assuming that business
unit is a separate entity, accounting records are kept only from the point of
view of the business unit and not the owners.
Example
Mr.
B starts a business as X & Co., accounts are to be prepared from the point
of view of X & Co., as if it was a different person from the owner.
This
concept applies to all the form of business organizations for the following
reasons;
Solution
to business and personal transactions of the owner.To ascertain the return on capital employed.
To ensure proper use of funds.
To hold title to property in the name of the firm.
To enter into business with outsiders.
Money Measurement
It is the medium of exchange. It provides
a uniform way to measure the value of goods services. It makes exchange more
efficient. Finally, money is a store of value. Money is one form in which wealth
can be maintained.
The accounting system uses money as
its basic unit of measurement. All business transactions are recorded in terms
of money; it is a useful way of converting accounting data into a common unit.
Under this concept,
only those transactions which can be measured in terms of money are to be
recorded in the books of account.
Problem with
Money Measurement
Stability in the value of money
Rs.
1 a year from now will buy the same
amount as it does today.
Factors of Vital Importance
Factors to the business are outside the
purview of accounting.
This is because they are matters of opinion
and cannot be expressed in monetary terms.
Conclusion
For the above two reasons, the money measurement
concept is not ideal. It is recognized by all accountants that the concept has
its limitations and inadequacies.
Accounting Concepts and Conventions
GAAP
set of rules can provide uniformity in the
Accounting system
Accounting procedure
Presentation of accounting results
Accounting
assumptions are those broad concepts that develop GAAP principles, upon which accounting
is based. Certain ideas and rules are assumed in account in order to provide a
unifying theoretical structure and internal logic of accounting.
The
assumptions are rule of the game and they have been developed
from common accounting practices.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Generally
accepted accounting principles are the conventions, rules and procedures necessary
to define accepted accounting practice at a particular time. These principles
provide a foundation for measuring and disclosing the results of business
transaction and events.
 GAAP
are conventional, that is, they become generally accepted by agreement rather
than by formal derivation from as se of postulates or basic concepts.
GAAP
are conventional, that is, they become generally accepted by agreement rather
than by formal derivation from as se of postulates or basic concepts.
How
GAAP Developed
The
principles are developed on the basis of experience, reason, custom, usage and
to a significant extent, practical necessity. These principles are widely used
and accepted that may be produced to underline and accounting statements.
Role
of Accountant
GAAP
instructs an Accountant what to do in the usual case when he has no reason to
doubt that the affairs of the organization are being honestly conducted. Since
he has reason to believe that this basic assumption is false, an entity
different situation confronts him.
Saturday, February 1, 2020
Reliability, Relevance, Understand-ability, Comparability in Accounting Information
Reliability
Accounting information should be
reliable. It gives the user confidence and trust. It is reasonable
representation of actual items or event that has occurred. Accounting
information should be error-free and neutral; an accountant’s bias must not
color his information.
Relevance
Accounting information must be
relevant to the user. It is relevant if it needs of the user in decision
making. Relevance is defined in the terms of the ability to affect a
decision-maker’s course of action.For information to be relevant, it must have some being on the decision being made. Relevant information should be capable of making difference in a decision by helping user of accounting information form predictions about the outcomes of past, present and future event.
Understand-ability
Understand-ability is the quality of accounting information that enables user to perceive its significant, i.e to understand the content and significance of accounting statements and reports. To have the characteristics of understand-ability, accounting information must be presented in a manger that users can understand, i.e it must be expressed in terminology that is understandable to the user.
It is necessary that user of the
accounting information must attain a minimum level of competence in
understanding the terminology user in accounting statements.
It is assumed that the users have
a basic knowledge of business accounting, and they will spend some time and
effort in studying the accounting statements. However, the accountant has a
basic responsibility to describe business transactions clearly and concisely.
Usefulness is enhanced in accounting information can be compared with similar information for the same organization at different times, and for different organizations at the same time. It enhances the value of accounting information.
Absoluteness of the accounting is
not of much use, it is the comparability that lens itself to proper decision
making.
To achieve comparability,
consistency and disclosure of accounting policies are necessary.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)